Sugar is one of the most common ingredients in modern diets. It is found not only in sweets and desserts but also in packaged foods, sauces, soft drinks, cereals, and even “healthy” snacks. While small amounts of sugar can be part of a balanced diet, consuming too much sugar regularly can negatively affect your body and overall health.
In this article, we will explore how sugar impacts your body, what happens when you eat too much, and how you can reduce sugar intake for a healthier lifestyle.
What Is Sugar and Why Do We Crave It?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that provides quick energy. There are two main types of sugar:
- Natural sugar: Found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy
- Added sugar: Added during processing, cooking, or packaging
Your brain and body naturally enjoy sugar because it provides fast energy and triggers the release of “feel-good” chemicals like dopamine. This is why sugary foods can feel addictive and difficult to stop eating.
How Sugar Affects Your Body Immediately
When you eat sugar, your body breaks it down into glucose. This glucose enters your bloodstream and causes a rise in blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Spike and Energy Crash
After eating sugary foods, you may feel a quick energy boost. However, this energy does not last long. Your body releases insulin to lower blood sugar, which can lead to a sudden drop. This is often called an “energy crash.”
Signs of a sugar crash include:
- Feeling tired or sleepy
- Headache
- Irritability
- Hunger soon after eating
- Difficulty focusing
How Sugar Impacts Your Weight and Metabolism
Sugar is high in calories but low in nutrients. It adds energy without providing important vitamins, minerals, or fiber.
Increased Fat Storage
When you consume excess sugar, your body stores the extra energy as fat. Over time, this can lead to weight gain, especially around the belly.
Increased Appetite and Cravings
Sugar can increase hunger by affecting hormones that control appetite. It can also cause cravings for more sugar, creating a cycle of overeating.
Sugar and Its Effect on Your Heart Health
Too much sugar can harm your heart and blood vessels.
Raises Risk of High Blood Pressure
High sugar intake may increase blood pressure and cause inflammation in the body.
Increases Bad Cholesterol
Excess sugar can raise triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood) and reduce good cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
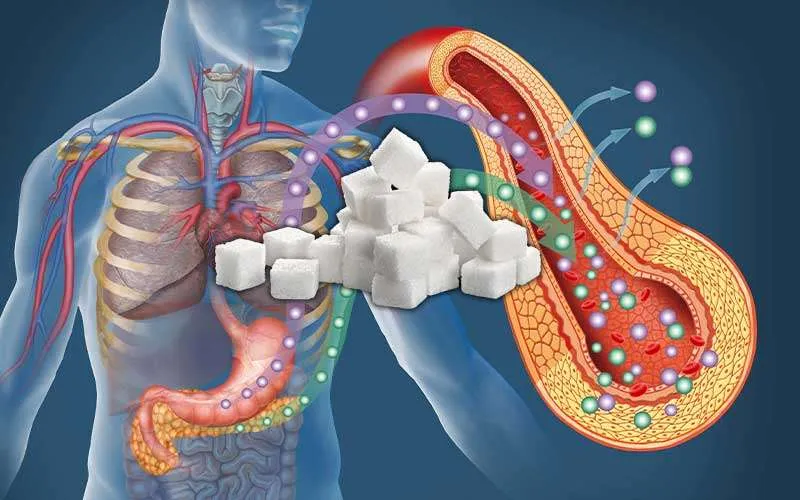
Sugar and Blood Sugar Problems (Diabetes Risk)
One of the biggest health concerns linked to sugar is its connection to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
What Is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin helps move glucose from the blood into cells for energy. When you eat too much sugar over time, your cells may stop responding properly to insulin. This is called insulin resistance.
How It Leads to Type 2 Diabetes
When insulin resistance increases, blood sugar stays high. Over time, this can lead to type 2 diabetes, which increases the risk of heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
Sugar and Your Skin Health
Sugar can affect your skin appearance and speed up aging.
Causes Acne Breakouts
High sugar intake can increase inflammation and hormonal changes that may lead to acne and oily skin.
Speeds Up Skin Aging
Sugar can damage collagen and elastin, which are proteins that keep your skin firm and youthful. This may cause:
- Wrinkles
- Sagging skin
- Dull complexion
Sugar and Your Teeth
Sugar is one of the biggest causes of tooth decay.
How Sugar Causes Cavities
Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar and produce acid. This acid damages tooth enamel and causes cavities over time.
Signs of poor dental health include:
- Tooth sensitivity
- Bad breath
- Cavities
- Gum problems
Sugar and Brain Health
Sugar affects your brain function, mood, and mental focus.
Mood Swings and Anxiety
Because sugar causes blood sugar spikes and crashes, it can lead to mood changes such as:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Stress
- Low mood
Poor Focus and Memory
Too much sugar may reduce concentration and can affect brain performance, especially when consumed daily.
Sugar and Your Digestive System
Many sugary foods are low in fiber, which is essential for healthy digestion.
Causes Poor Gut Health
High sugar can feed harmful bacteria in the gut, which may lead to:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Constipation
- Unhealthy digestion
Hidden Sources of Sugar You Should Know
Many people think sugar only comes from sweets, but added sugar is found in many everyday foods.
Common hidden sources include:
- Soft drinks and energy drinks
- Packaged fruit juices
- Breakfast cereals
- Flavored yogurt
- Ketchup and sauces
- Bakery items
- Protein bars and snacks
Always check food labels for ingredients like:
- Corn syrup
- Glucose syrup
- Sucrose
- Dextrose
- Maltose
How to Reduce Sugar Intake in Daily Life
Reducing sugar does not mean removing all sweetness from your life. It means making smarter choices.
Choose Natural Sugar Options
Instead of sweets, choose:
- Fresh fruits
- Dates (in moderation)
- Honey (small amount)
Drink More Water
Replace sugary drinks with:
- Water
- Lemon water
- Herbal tea
- Green tea
Read Food Labels
Avoid products with high added sugar and long ingredient lists.
Eat More Protein and Fiber
Protein and fiber help control cravings and keep you full.
Good options include:
- Eggs
- Lentils
- Chicken
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
Conclusion
Sugar may taste good, but too much sugar can harm your body in many ways. It can lead to weight gain, energy crashes, heart problems, diabetes risk, acne, tooth decay, and poor mental focus. The best way to protect your health is to limit added sugar and choose whole, nutrient-rich foods. By making small changes like drinking more water, eating more fruits and vegetables, and reading food labels, you can reduce sugar intake and improve your overall health over time.